Engineering trust, accelerating growth and sculpting change are the three overarching trends on the Gartner Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2021 that will drive organisations to explore emerging technologies such as nonfungible tokens (NFT), sovereign cloud, data fabric, generative AI and composable networks to help secure competitive advantage.
“Technology innovation is a key enabler of competitive differentiation and is the catalyst for transforming many industries. Breakthrough technologies are continually appearing, challenging even the most innovative organizations to keep up,” says Brian Burke, research vice-president at Gartner.
“Leading organisations will lean on the emerging technologies in this year’s Hype Cycle to build trust and new growth opportunities against a background of continued strategic change and economic uncertainty.”
The Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies is unique among most Gartner Hype Cycles because it distils insights from more than 1 500 technologies into a succinct set of “must know” emerging technologies and trends that show promise in delivering a high degree of competitive advantage over the next five to 10 years.
Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2021
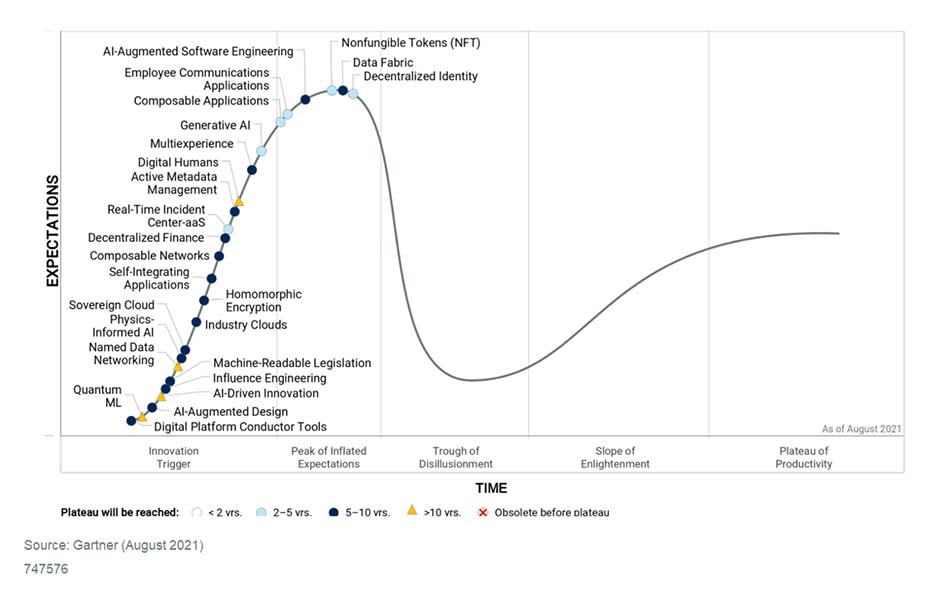
Source: Gartner (August 2021)
“As organisations continue their focus on digital business transformation, they must accelerate change and cut through the hype surrounding emerging technologies,” says Melissa Davis, research vice-president at Gartner.
“This Hype Cycle provides a high-level view of important emerging trends that organisations must track, as well as the specific technologies that must be monitored through the themes of Trust, Growth and Change,” says Philip Dawson, research vice-president at Gartner.
Three Themes of Emerging Technology Trends
Engineering Trust: Trust demands security and reliability. However, it can also extend to building innovations as a resilient core and foundation for IT to deliver business value. This foundation must consist of engineered, repeatable, trusted, proven and scalable working practices and innovations.
For example, the market for digital and cloud technology and services is currently dominated by US and Asian providers. As a result, many European companies store their data in these regions, creating political uneasiness as well as concerns about retaining data control and complying with local regulations.
Countries can engage a sovereign cloud to achieve digital and data sovereignty, which will in turn provide legal requirements to apply data protection controls, residency requirements, protectionism and intelligence gathering.
The technologies to watch to engineer trust are sovereign cloud, NFT, machine-readable legislation, decentralised identity, decentralised finance, homomorphic encryption, active metadata management, data fabric, real-time incident center and employee communications applications.
Accelerating Growth: After the trusted core business is established, recovery and growth can happen. Organisations should balance technology risk with the appetite for business risk to ensure near-term objectives are attainable. Once the innovation-led core is scaling, accelerated growth extends delivery and value.
For example, generative AI is an emerging technology that the pharmaceutical industry is using to help reduce costs and time in drug discovery. Gartner predicts that by 2025, more than 30% of new drugs and materials will be systematically discovered using generative AI techniques. Generative AI will not only augment and accelerate design in many fields; it also has the potential to “invent” novel designs that humans may have otherwise missed.
To accelerate growth, the following technologies should be explored: multiexperience, industry cloud, AI-driven innovation, quantum machine learning (ML), generative AI and digital humans.
Sculpting Change: Change is traditionally disruptive and often is tied to chaos, but organisations can use innovations to sculpt change and bring order to chaos. The art is to anticipate and auto-tune to the needs of change.
For example, composable business applications enable a better match of application experiences to a changing, operational business context. Composable business, founded on composable application technology and built with composable thinking, positions organisations to recognize and exploit business opportunities, respond to unexpected disruptions, and meet customers’ changing demands at their pace, retaining their loyalty.
Organisations looking to sculpt change should consider composable applications, composable networks, AI-augmented design, AI-augmented software engineering, physics-informed AI, influence engineering, digital platform conductor tools, named data networking and self-integrating applications.
