In the coming days, NASA’s Perseverance rover is expected to begin building the first sample depot on another world. This will mark a crucial milestone in the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign, which aims to bring Mars samples to Earth for closer study.
The depot-building process starts when the rover drops one of its titanium sample tubes carrying a chalk-size core of rock from its belly 88,8cm onto the ground at an area within Jezero Crater nicknamed “Three Forks”.
Over the course of 30 or so days, Perseverance will deposit a total of 10 tubes that carry samples representing the diversity of the rock record in Jezero Crater.
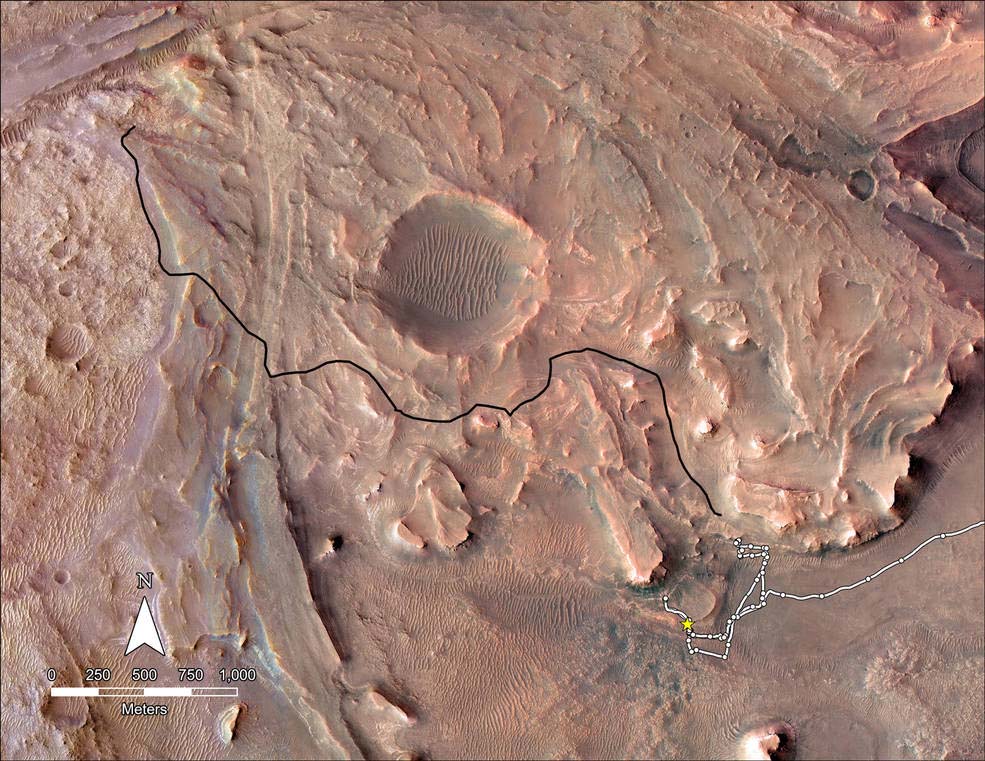
This map shows the planned route NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover will take across the top of Jezero Crater’s delta in 2023. The rover’s planned route is in black while the ground it already covered is in white.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The rover has been taking a pair of samples from each of its rock targets. Half of every pair will be deposited at Three Forks as a backup set, and the other half will remain inside Perseverance, which will be the primary means to convey the collected samples to the Mars launch vehicle as part of the campaign.
“The samples for this depot – and the duplicates held aboard Perseverance – are an incredible set representative of the area explored during the prime mission,” says Meenakshi Wadhwa, the Mars Sample Return program principal scientist from Arizona State University. “We not only have igneous and sedimentary rocks that record at least two and possibly four or even more distinct styles of aqueous alteration, but also regolith, atmosphere, and a witness tube.”

Shown here is a representation of the 21 sample tubes (containing rock, regolith, atmosphere, and witness materials) that have been sealed to date by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover. The samples Perseverance is depositing into a depot are highlighted in green.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
How to build a depot
One of the first requirements to build a sample depot on Mars is to find a level, rock-free stretch of terrain in Jezero Crater where there’s room for each tube to be deposited.
“Up to now, Mars missions required just one good landing zone; we need 11,” said Richard Cook, Mars Sample Return program manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “The first one is for the Sample Retrieval Lander, but then we need 10 more in the vicinity for our Sample Recovery Helicopters to perform takeoffs and landings, and driving too.”

NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture this rocky hilltop nicknamed “Rockytop” on July 24, 2022, the 507th Martian day, or sol, of the mission.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS
After settling on a suitable site, the campaign’s next task was to figure out exactly where and how to deploy the tubes within that location. “You can’t simply drop them in a big pile because the recovery helicopters are designed to interact with only one tube at a time,” says Cook.
The helicopters are intended to serve as a backup, just like the depot. To ensure a helicopter could retrieve samples without disturbing the rest of the depot or encountering any obstructions from the occasional rock or ripple, each tube-drop location will have an “area of operation” at least 5,5m in diameter. To that end, the tubes will be deposited on the surface in an intricate zigzag pattern, with each sample 5m to 15m apart from one another.
The depot’s success will depend on accurate placement of the tubes – a process that will take over a month. Before and after Perseverance drops each tube, mission controllers will review a multitude of images from the rover. This assessment will also give the Mars Sample Return team the precise data necessary to locate the tubes in the event of the samples becoming covered by dust or sand before they are collected.
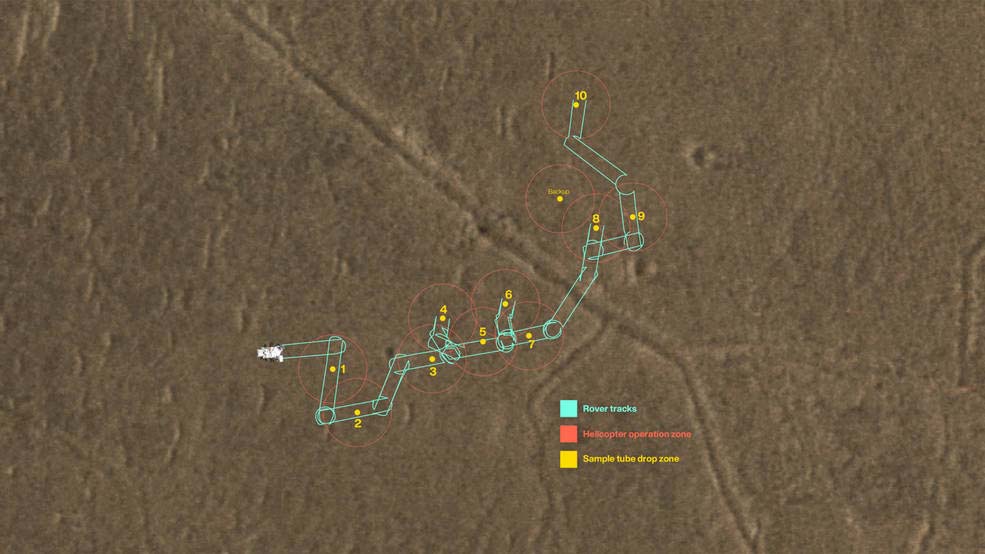
This map shows where NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover will be dropping 10 samples that a future mission could pick up. The orange circles represent areas where a Sample Recovery Helicopter could safely operate to acquire the sample tubes.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Perseverance’s extended mission
Perseverance’s prime mission will conclude on 6 January 2023 – one Mars year (about 687 Earth days) after its 18 February 2021 landing.
“We will still be working the sample depot deployment when our extended mission begins on 7 January, so nothing changes from that perspective,” says Art Thompson, Perseverance’s project manager at JPL. “However, once the table is set at Three Forks, we’ll head to the top of the delta. The science team wants to take a good look around up there.”
Called the Delta Top Campaign, this new science phase will begin when Perseverance finishes its ascent of the delta’s steep embankment and arrives at the expanse that forms the upper surface of the Jezero delta, probably sometime in February. During this approximately eight-month campaign, the science team will be on the lookout for boulders and other materials that were carried from elsewhere on Mars and deposited by the ancient river that formed this delta.
This short animation features key moments of NASA and ESA’s Mars Sample Return campaign, from landing on Mars and securing the sample tubes to launching them off the surface and ferrying them back to Earth.
Credits: NASA/ESA/JPL-Caltech/GSFC/MSFC
“The Delta Top Campaign is our opportunity to get a glimpse at the geological process beyond the walls of Jezero Crater,” says JPL’s Katie Stack Morgan, deputy project scientist for Perseverance. “Billions of years ago a raging river carried debris and boulders from miles beyond the walls of Jezero. We are going to explore these ancient river deposits and obtain samples from their long-traveled boulders and rocks.”
More About the Mission
A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including caching samples that may contain signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith.
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA, would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
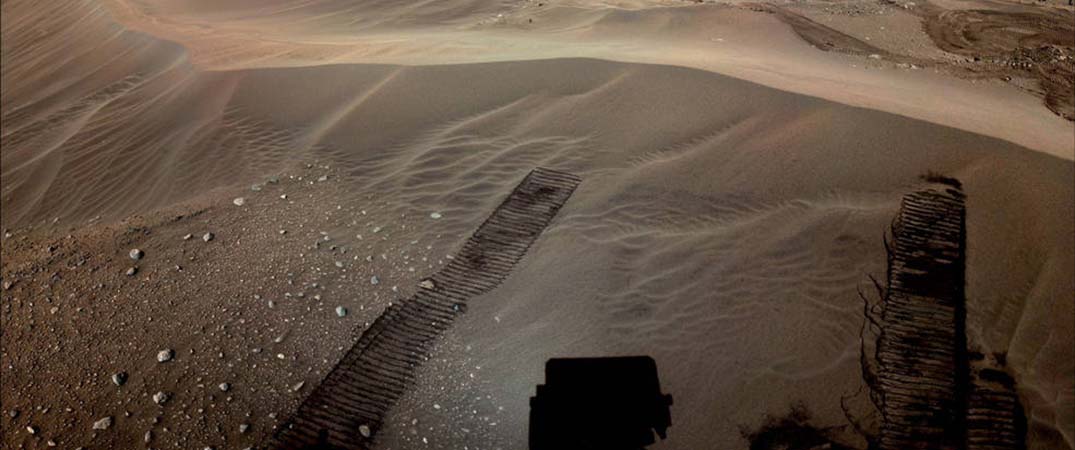
Featured picture: The location where NASA’s Perseverance will begin depositing its first cache of samples is shown in this image taken by the Mars rover on Dec. 14, 2022, the 646th Martian day, or sol, of the mission.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS

